Imagine waking up one morning to find an unsightly pimple right on your forehead. We’ve all been there, but have you ever wondered what actually causes these pesky blemishes to show up on our skin? In this article, we’ll explore the scientific explanations behind the occurrence of pimples, shedding light on the factors that lead to their formation and demystifying the age-old question of why they appear. So, get ready to embark on a journey into the world of science and discover the secrets behind those pesky pimples!
Introduction
Pimples are a common skin condition that affects many teenagers. They can have a significant impact on self-esteem and mental well-being. Understanding the scientific causes of pimples is essential to prevent and treat this frustrating skin issue.
Definition of Pimples
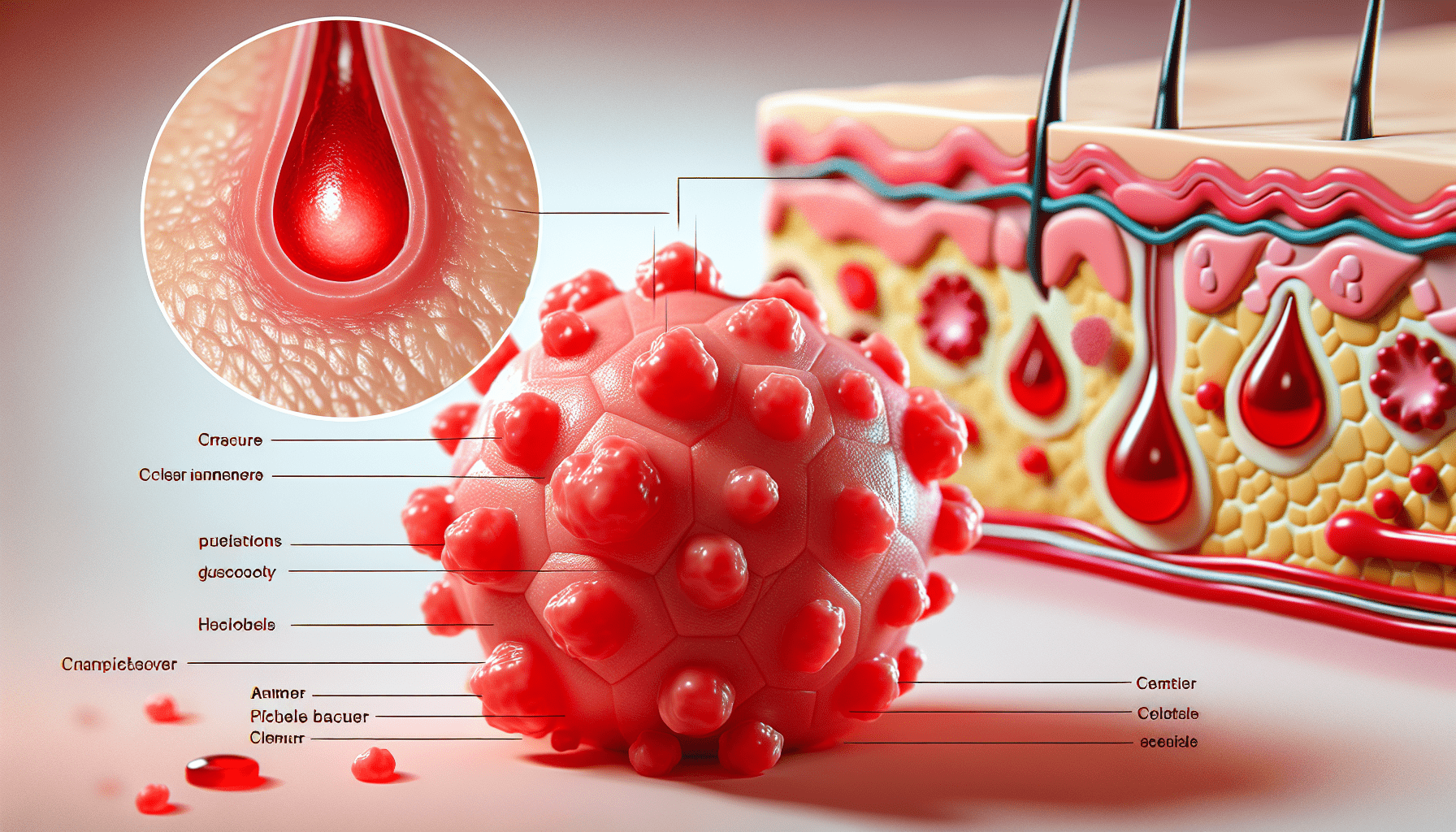
Pimples, also known as acne vulgaris, are inflammatory skin lesions that occur when the pores of the skin become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. They typically manifest as red bumps or whiteheads on the face, chest, and back.
Common Occurrence in Teenagers
Pimples are especially prevalent during adolescence due to hormonal changes that occur during this time. Approximately 85% of teenagers experience pimples to some degree, making it a common skin concern among this age group.
Impact on Self-Esteem and Mental Well-Being
Having pimples may negatively affect a person’s self-esteem and mental well-being. Teenagers, in particular, may experience embarrassment and a decreased sense of self-confidence as a result of their appearance. It is important to address and understand the causes of pimples to alleviate these emotional challenges.
Understanding Pimples
To understand the causes of pimples, it is necessary to examine the various factors involved in their formation.
Definition of Pimples
As mentioned earlier, pimples are inflammatory skin lesions that develop when the pores become clogged. They can appear as whiteheads, blackheads, or inflamed red bumps.
Sebaceous Glands and Hair Follicles
Pimples develop primarily in areas that have a high concentration of sebaceous glands and hair follicles, such as the face, chest, and back. These glands produce sebum, an oily substance that helps lubricate the skin and hair.
Role of Hormones in Pimple Formation
Hormones play a significant role in the development of pimples. During puberty, hormonal changes, particularly an increase in androgen levels, stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum. This excess sebum production contributes to the formation of pimples.
Factors Contributing to Pimple Formation
Several factors contribute to the formation of pimples. Understanding these factors is essential to prevent and manage this common skin concern.
Excess Sebum Production
Sebaceous glands play a crucial role in pimple formation as they produce sebum. Androgens, a type of hormone, stimulate these glands to increase sebum production. The excess sebum can lead to clogged pores and the development of pimples.
Clogging of Hair Follicles
Pimples develop when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. This process starts with the formation of comedones, which can be either open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). Accumulation of dead skin cells and blockage by sebum and debris can further contribute to the clogging of hair follicles.
Bacterial Colonization
The presence of the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) on the skin plays a significant role in pimple formation. P. acnes tends to flourish in clogged pores and can aggravate inflammation. It releases enzymes that break down sebum, triggering an inflammatory response in the skin.
Inflammation
When the immune system detects the presence of bacteria in clogged pores, it initiates an inflammatory response. This response involves the release of inflammatory mediators called cytokines, which lead to redness and swelling. Inflammation is responsible for the characteristic appearance of inflamed pimples.
Contributing Factors to Pimple Formation
While the scientific causes of pimples primarily revolve around excess sebum production, clogging of hair follicles, bacterial colonization, and inflammation, several other factors can contribute to their development.
Genetics
Genetics play a role in determining an individual’s predisposition to acne. Some people have inherited genes that make them more prone to developing pimples. Understanding one’s genetic makeup can provide insight into their susceptibility to pimples.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty and menstruation, can contribute to the development of pimples. These fluctuations increase sebum production, making the skin more prone to clogging and the formation of pimples.
Stress
Stress has been linked to the worsening of acne symptoms. When we are under stress, the body produces more cortisol, a stress hormone that can contribute to increased sebum production. Additionally, stress may exacerbate inflammation and impair the body’s ability to fight off bacteria, worsening pimple formation.
Diet
While diet alone does not directly cause pimples, certain foods can exacerbate acne symptoms in some individuals. High glycemic index foods, dairy products, and foods rich in saturated and trans fats have been associated with an increased risk of pimples in some studies. However, more research is needed to establish a definitive link between diet and pimples.
Poor Skincare Habits
Inadequate skincare practices, such as not removing makeup before bed or using harsh products, can contribute to the development of pimples. These practices can lead to clogged pores and irritate the skin, exacerbating pimple formation.
Conclusion
Pimples are a common skin condition that affects teenagers and can have a significant impact on self-esteem and mental well-being. Understanding the scientific causes of pimples, such as excess sebum production, clogging of hair follicles, bacterial colonization, inflammation, and other contributing factors like genetics, hormonal changes, stress, diet, and skincare habits, is essential for prevention and treatment. By promoting skin health and well-being through proper skincare practices, lifestyle modifications, and seeking professional advice when necessary, individuals can effectively manage and prevent the formation of pimples.