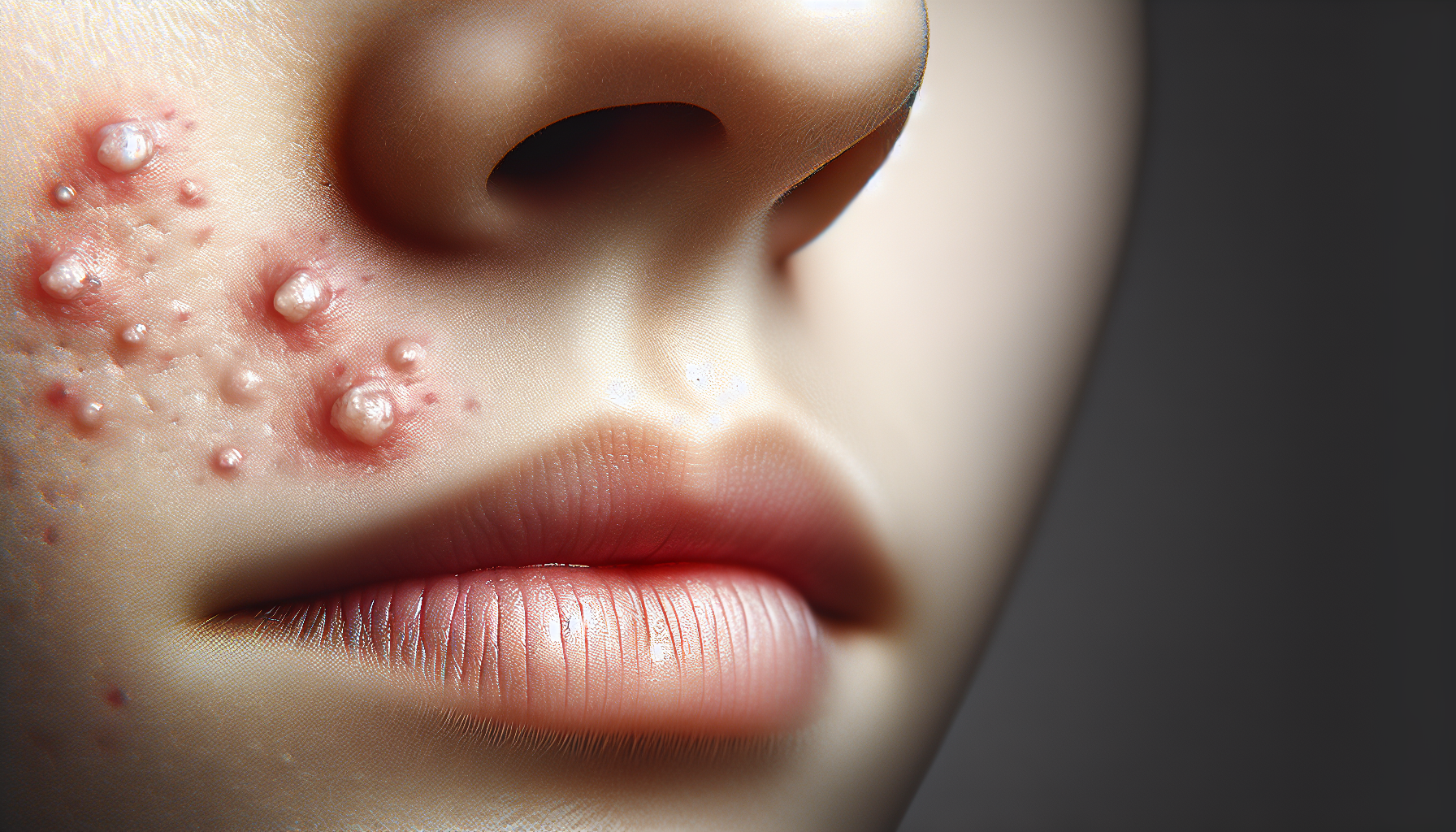
If you’ve ever found yourself silently asking this question while desperately searching for a solution to your persistent face acne, you’re not alone. Dealing with these frustrating blemishes can be a challenge, leaving you feeling self-conscious and longing for clear, smooth skin. But fear not, for there are indeed effective strategies that can help you win the battle against face acne. From adopting a diligent skincare routine to making lifestyle changes, this article will guide you through practical tips, empowering you to take control of your acne and unleash your radiant complexion. So say goodbye to those pesky pimples and hello to a confident, acne-free you.
Understanding the Causes of Face Acne
Acne, a common skin condition, occurs when the hair follicles on your face become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and other blemishes. Understanding the underlying causes of acne can help you effectively manage and prevent breakouts.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes play a significant role in the development of face acne, particularly during puberty. Increased production of androgens stimulates the sebaceous glands, leading to excessive oil production. This excess oil can clog the pores and promote acne formation. Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during menstrual cycles or pregnancy, can also contribute to breakouts.
Excessive Oil Production
Overproduction of oil, known as sebum, can contribute to the development of acne. The sebaceous glands produce sebum to keep the skin lubricated, but when too much sebum is produced, it can mix with dead skin cells and become trapped in the hair follicles, resulting in acne.
Clogged Pores
When the hair follicles become blocked with oil, dead skin cells, and other impurities, the pores become clogged. This can create a favorable environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to inflammation and the formation of acne.
Bacteria
The skin is home to a type of bacteria called Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes). In individuals with acne-prone skin, these bacteria can multiply rapidly in clogged pores, triggering an immune response and causing inflammation. This inflammation leads to the redness, swelling, and discomfort associated with acne breakouts.
Skin Irritation
Excessive skin irritation or friction can worsen acne or trigger new breakouts. Scrubbing the face too harshly, using abrasive skincare products, or wearing tight-fitting clothing can all contribute to skin irritation and inflammation, exacerbating existing acne or creating new blemishes.
Identifying Different Types of Face Acne
Not all acne is the same, and understanding the various types can help you tailor your skincare routine and treatment methods accordingly. Here are some common types of face acne:
Whiteheads
Whiteheads are non-inflammatory acne lesions that form when the hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. The trapped material remains beneath the skin’s surface, resulting in tiny white or flesh-colored bumps.
Blackheads
Similar to whiteheads, blackheads are non-inflammatory acne lesions. However, these lesions are open to the skin’s surface, and the trapped material oxidizes, giving them their characteristic dark appearance. Blackheads can be easily identified by their black or dark color.
Papules
Papules are small, inflamed, raised bumps on the skin that are usually red or pink in color. They occur when the hair follicles become inflamed due to the presence of bacteria and excess oil.
Pustules
Pustules are another form of inflamed acne lesion. They are characterized by their white or yellow centers surrounded by a red base. Pustules contain pus and can be painful or tender to the touch.
Nodules
Nodules are large, solid, and painful acne lesions that develop deep within the skin. They can be red or flesh-colored and are caused by the buildup of oil, bacteria, and dead skin cells. Nodular acne often requires professional treatment as they can lead to scarring if improperly managed.
Cysts
Cystic acne is the most severe form of acne and is characterized by large, painful, deep-rooted cysts beneath the skin’s surface. These cysts are filled with fluid, pus, and sometimes blood. Treating cystic acne requires medical intervention to prevent scarring and manage the infection properly.
Maintaining a Healthy Skincare Routine
Establishing a consistent and effective skincare routine is crucial for managing and preventing acne breakouts. Here are some essential steps to incorporate into your daily regimen:
Cleansing
Cleansing your face twice daily, in the morning and evening, helps remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities from the skin’s surface. Opt for a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser specifically formulated for acne-prone skin to avoid further irritation.
Exfoliating
Exfoliating the skin once or twice a week can help remove dead skin cells that can contribute to clogged pores. Look for exfoliators with gentle ingredients like salicylic acid or fruit enzymes to avoid stripping the skin of its natural moisture.
Toning
Using a toner after cleansing can help balance the skin’s pH levels, remove any residual dirt or cleanser, and tighten the pores. Look for toners with ingredients like witch hazel or tea tree oil, known for their antibacterial properties.
Moisturizing
Contrary to popular belief, moisturizing is essential even for acne-prone skin. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers that provide hydration without clogging the pores. This step helps maintain the skin’s barrier function and prevents excessive dryness that can trigger more oil production.
Protecting
Always protect your skin from harmful UV rays by applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Sun exposure can worsen acne and lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or scarring.
Choosing the Right Products
Using the right products is crucial for managing and preventing acne breakouts. Here are some key considerations when selecting skincare products:
Non-Comedogenic Products
Opt for non-comedogenic products that are specifically formulated to not clog the pores. These products are less likely to exacerbate acne or cause further breakouts.
Oil-Free Products
Using oil-free formulations can help reduce excessive oil production and prevent pore blockage. Look for products labeled as “oil-free” to minimize the risk of acne flare-ups.
Gentle Cleansers
Choose gentle cleansers that won’t strip the skin’s natural moisture barrier or cause irritation. Harsh cleansers can disrupt the skin’s balance, leading to increased oil production and breakouts.
Salicylic Acid Products
Salicylic acid is a common ingredient in acne skincare products. It helps exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and reduce inflammation. Incorporating salicylic acid products into your routine can aid in managing acne.
Benzoyl Peroxide Products
Benzoyl peroxide is another effective ingredient for combating acne. It works by reducing P. acnes bacteria and removing dead skin cells, helping to prevent new breakouts. However, benzoyl peroxide may cause dryness and irritation in some individuals, so start with a lower concentration and gradually increase if needed.
Retinoid Products
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, are known for their anti-acne effects. They help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and promote cell turnover, resulting in clearer skin. However, retinoids can be irritating, so it’s important to start with a low concentration and gradually increase over time.
Natural Remedies
While not supported by scientific evidence, some individuals find relief from acne by using natural remedies. Tea tree oil, aloe vera, and green tea extract are popular options known for their antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. However, it’s essential to patch test these remedies and discontinue use if any adverse reactions occur.
Avoiding Harsh Skin Irritants
Certain substances and practices can irritate the skin, worsening existing acne or triggering new breakouts. Here are some common irritants to avoid:
Products with Alcohol
Skincare products that contain high concentrations of alcohol can strip the skin’s natural oils and cause dryness. This can lead to increased oil production as the skin tries to compensate, potentially worsening acne.
Fragranced Products
Fragrances, whether natural or synthetic, can irritate sensitive or acne-prone skin. These ingredients can trigger inflammation and exacerbate existing breakouts. Look for fragrance-free products to minimize the risk of irritation.
Harsh Scrubs
Avoid using harsh exfoliators or physical scrubs that contain irregularly shaped particles, as they can cause micro-tears in the skin and worsen inflammation. Opt for gentle exfoliation methods like chemical exfoliants instead.
Tight Clothing
Wearing tight-fitting clothing, such as hats or collars, can trap sweat and oil against the skin, leading to increased acne breakouts. Opt for looser clothing made from breathable fabrics to reduce friction and allow the skin to breathe.
Dirty Pillowcases and Towels
Dirty pillowcases and towels can harbor bacteria, oil, and dead skin cells, which can transfer to your face and exacerbate acne. Ensure you regularly wash these items to maintain cleanliness and minimize the risk of acne flare-ups.
Practicing Proper Face Washing Techniques
While washing your face is an essential part of any skincare routine, practicing proper techniques can optimize its effectiveness and prevent further irritation. Here are some tips for washing your face:
Wash Your Face Twice Daily
Wash your face in the morning and evening to remove dirt, excess oil, and impurities that accumulate throughout the day and while you sleep. Cleansing too frequently can strip the skin’s natural moisture, leading to increased oil production.
Use Lukewarm Water
Avoid using hot water while cleansing your face, as it can strip the skin’s natural oils and cause dryness. Opt for lukewarm water instead, as it effectively removes dirt without damaging the skin.
Gentle Cleansing Motions
Use gentle, circular motions to cleanse your face, avoiding harsh scrubbing that can irritate the skin and worsen acne. Be mindful of the pressure you apply and always treat your skin with care.
Avoid Over-Washing
While it may be tempting to wash your face repeatedly throughout the day, over-washing can disrupt the skin’s natural balance, leading to increased oil production and potential flare-ups. Stick to washing your face twice daily unless advised otherwise by a dermatologist.
Be Mindful of Water Temperature
After cleansing, rinse your face with cool water to close the pores and refresh the skin. Hot water can further irritate the skin and lead to inflammation, while cool water can help soothe and reduce redness.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
While diet alone may not be the sole cause of acne, certain foods can exacerbate breakouts in some individuals. Incorporating some dietary changes may help manage acne. Here are some tips:
Avoiding High-Glycemic Foods
High-glycemic foods, such as white bread, sugary snacks, and processed cereals, can cause blood sugar spikes and promote inflammation in the body. This inflammation can worsen acne breakouts. Opt for low-glycemic foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables instead.
Reducing Dairy Consumption
Some studies have suggested a link between dairy consumption and acne flare-ups. Dairy products contain hormones and growth factors that may contribute to increased oil production and clogged pores. If you suspect dairy is worsening your acne, consider reducing your consumption or trying dairy alternatives.
Eating Foods Rich in Antioxidants
Antioxidants help fight inflammation and protect the body against free radicals that can damage the skin. Incorporate foods like berries, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds into your diet to provide your body with a rich supply of antioxidants.
Increasing Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce acne-related inflammation. Include foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your diet to boost your omega-3 intake.
Hydrating Properly
Staying properly hydrated is essential for overall skin health. Water helps flush out toxins and keeps the skin hydrated from within. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day to maintain optimal hydration levels.
Limiting Stress and Getting Enough Sleep
Stress and lack of sleep can contribute to hormonal imbalances, inflammation, and increased oil production, all of which can worsen acne breakouts. Practicing stress management techniques and prioritizing sufficient sleep can benefit your skin. Here are some tips:
Stress Management Techniques
Engage in activities that help reduce stress, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies you enjoy. Finding healthy outlets for stress can help prevent its negative impact on your skin.
Getting Adequate Sleep
Achieving an adequate amount of sleep each night is crucial for overall health, including skin health. Aim for seven to eight hours of quality sleep to allow your body time to repair and regenerate, helping to improve your skin’s condition.
Relaxation Exercises
Incorporate relaxation exercises into your daily routine, such as taking short breaks to stretch, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in activities that bring you joy. These exercises can help alleviate stress and promote a healthy mindset.
Balancing Work and Personal Life
Finding a healthy balance between work or school obligations and personal life is crucial for managing stress levels. Prioritize self-care activities and ensure you have time to relax and unwind.
Seeking Professional Advice
If you’re struggling to manage your acne or experiencing severe breakouts, it may be beneficial to seek professional advice from a dermatologist. They can provide personalized recommendations and treatments based on your specific skin type and concerns. Here are some options they may suggest:
Dermatologist Consultation
An initial consultation with a dermatologist can help assess your acne and determine the best course of action. They will evaluate your skin, discuss your medical history, and recommend suitable treatments.
Prescription Medication
Dermatologists may prescribe medications, such as oral antibiotics, hormonal treatments, or isotretinoin, to address moderate to severe acne. These medications work internally to target the root causes of acne.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, such as prescription-strength retinoids or antibiotics, may be recommended to reduce inflammation and unclog pores. These treatments are typically applied directly to the skin and can be effective for milder forms of acne.
Oral Medications
In some cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral medications, such as birth control pills or spironolactone, to regulate hormonal imbalances and manage acne. These medications require a doctor’s prescription and close monitoring.
Procedures and Treatments
Dermatologists may offer various procedures and treatments, such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy, to address acne and acne scarring. These treatments aim to renew the skin’s surface, reduce inflammation, and minimize the appearance of scars.
Professional Extraction
For stubborn acne lesions or severe breakouts, dermatologists can perform professional extractions to safely and effectively remove trapped debris and bacteria from the pores. This procedure helps alleviate inflammation and promote healing.
Dealing with Acne Scarring
Acne scars can have a significant impact on one’s self-esteem, but there are treatment options available to improve their appearance. Here are some common methods for addressing acne scarring:
Topical Scar Treatments
Topical scar treatments, such as silicone gels, vitamin C serums, or bio-oil, can help fade acne scars over time. These products are typically applied directly to the affected areas and work by promoting collagen production and skin regeneration.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layers and promote new skin cell growth. This process helps improve the appearance of acne scars, but multiple treatments may be necessary for optimal results.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that uses a special device to gently exfoliate the skin. It helps to reduce the appearance of acne scars by removing the top layers of skin and promoting collagen production.
Laser Treatments
Laser treatments, such as fractional laser resurfacing or intense pulsed light therapy (IPL), can improve the appearance of acne scars by stimulating collagen production and reducing skin discoloration. These treatments are typically performed by dermatologists or skincare professionals.
In conclusion, understanding the causes of face acne is essential for its effective management and prevention. Hormonal changes, excessive oil production, clogged pores, bacteria, and skin irritation all contribute to acne development. By identifying the different types of face acne and incorporating a comprehensive skincare routine, individuals can effectively manage their breakouts. Choosing the right products, avoiding harsh skin irritants, practicing proper face washing techniques, maintaining a healthy diet, limiting stress, and seeking professional advice when necessary are all key factors in achieving clear and healthy skin. Remember, treating acne is a process that requires patience and consistency, but with the right approach, acne breakouts can be effectively controlled, and acne scarring can be minimized.